Picture a bottle and think about how it gets narrower at the neck to restrict the flow coming out.
A process bottleneck is no different. It restricts the flow of that process.
The trick to streamlining processes to boost productivity is to identify bottlenecks as soon as possible. Unfortunately, that’s not always as easy as it seems.
The problem is that bottlenecks aren’t always obvious — especially if they’ve been around for a long time.
You may not realize that Janet in accounting is slowing down financial audits, if Janet in accounting has always done the audits. You might only realize that Janet’s the bottleneck once you add Mary to help and Mary works twice as fast.
It’s vital, then, to know how to identify bottlenecks on an ongoing basis as part of productive business process analysis. Otherwise you’re in danger of slowing down processes or halting them altogether.
In this article, you’ll learn what a bottleneck looks and feels like and how to identify bottlenecks before they disrupt your business.
What’s the Problem with Bottlenecks?
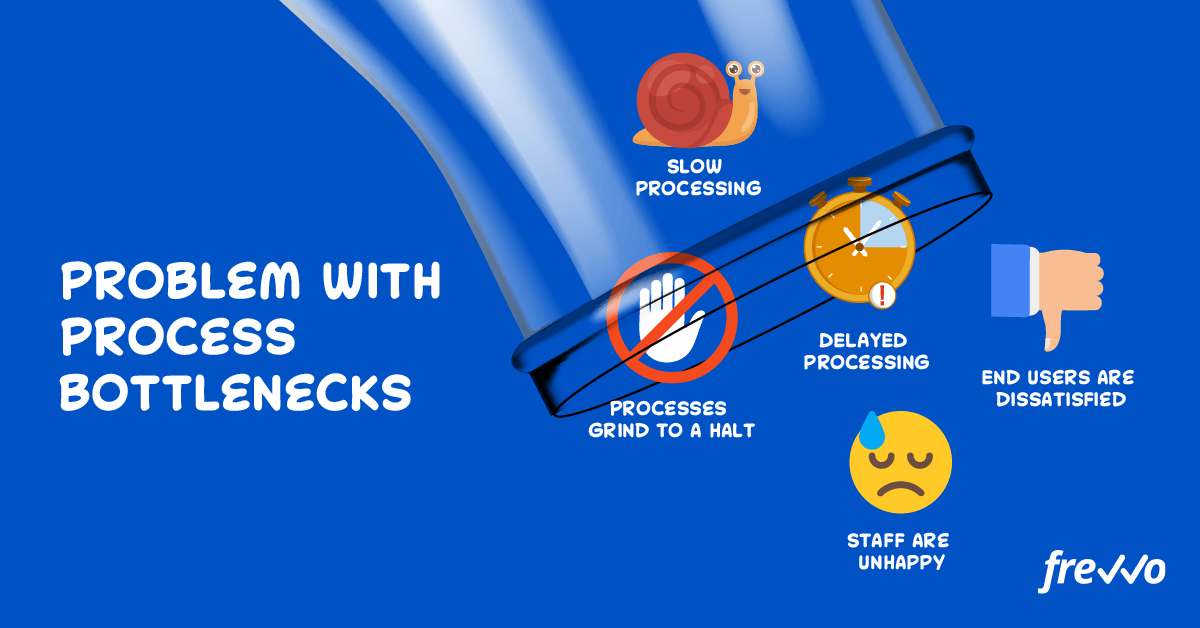
Bottlenecks are the reasons that your processes are less efficient. In short, this means that your processes take longer, cost more, and produce less.
Firstly, bottlenecks slow down processes or can halt them completely.
Picture a fully-booked restaurant. Suddenly, both servers call in sick last minute.
This halts the process since there’s nobody to take orders or deliver the food to tables.
You can send your line cooks out to do the job but their lack of training makes them slower and increases mistakes. Plus, since the line cooks are now taking orders, they’re slower to cook the food.
Cost is another issue. Bottlenecks are expensive as you end up shelling out extra cash to deal with delays or remedy issues.
In the restaurant scenario, you might end up giving customers money back to compensate for bad service and incorrect orders.
Obviously, these kinds of bottlenecks affect your company’s relationship with the end user.
Bottlenecks can result in loss of customer loyalty and bad reviews, harming your firm’s reputation. One look at Tripadvisor shows you how bottlenecks would affect our hypothetical restaurant.
All this culminates in an unhappy team.
Staff members feel overworked, underpaid, and underappreciated — a one-way ticket to high staff turnover.
How to Identify Bottlenecks in Your Processes
Identifying a workflow bottleneck early can help to streamline your processes before the results cause irreparable harm to your operations, team, and customer base.
If you want to know how to identify bottlenecks in your processes, follow these steps.
1. Map your process
In the first step, you need to map out the stages of the process you’re dealing with. By mapping out the stages that your staff go through, you can more clearly see where hold-ups happen.
Mapping basics
There are several process mapping tools to visualize your processes, but each follows a similar basic pattern.
First you need to define the process. This means understanding the boundaries of what’s included. Mostly this means understanding where the process starts and ends and when this process occurs.
Next, you need to identify the stakeholders. Who starts the chain (supplier) and who does the process end with (customer)? Who moves the process through each phase and who is it passed on to at each stage?
Now, map what happens through each phase of the process. Note how long each phase lasts and what resources are used and produced. You’ll also want to mark down how you measure the completion of each stage and how you hold those stakeholders accountable.
Last, map the conditional business rules used throughout the process. For example, a supervisor may approve deals under $5K, but a manager may approve deals over this sum.
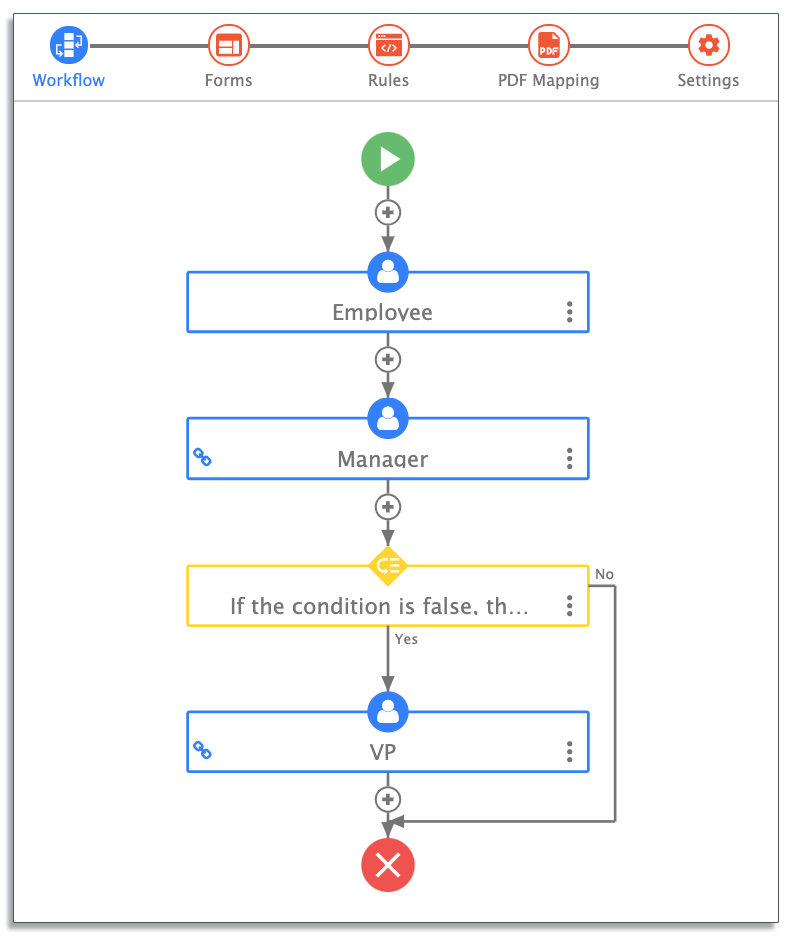
Business process model and notation
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a standard for mapping and visualizing business processes in a flowchart style.
Designed to be understandable by everyone in the business, this standard notation form shows what occurs and by whom, with conditional rules applied as tangential branches.
2. Know the types of bottlenecks
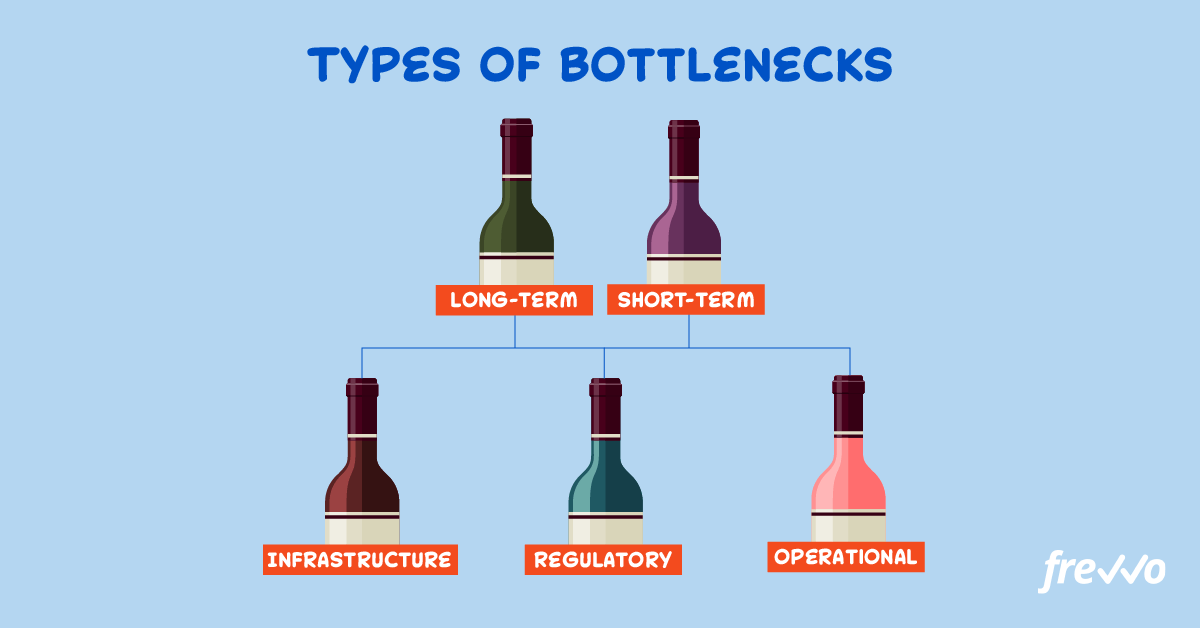
Bottleneck management relies on you knowing what kinds of bottlenecks to look for.
You’ll notice some bottlenecks right away as they’ll immediately impact your business like a pile-up on a highway.
However, some bottlenecks aren’t so obvious.
Sometimes the effects build up over time, like limescale in a kettle. Alternatively, super-efficient phases in the process may cover the inefficiencies elsewhere.
Knowing the different types of bottlenecks that can occur helps you to recognize the symptoms of those hold-ups early.
Long term bottlenecks
Long term or chronic bottlenecks are problems that occur all the time and are usually grandfathered in.
While these bottlenecks may not be obvious at first, the cumulative effect creates inefficiency over time.
Imagine the minute hand on a clock was a second slow every hour. You wouldn’t notice it at first, but over time, the clock would become late by hours.
The problem with long term bottlenecks is that they’re hard to identify as they’ve often been going on forever and have become an accepted part of the process.
In fact, your staff will often come to accept an existing bottleneck as a longer part of the process because that’s how it’s always been done — and they can’t imagine an alternative.
A typical example of this is manual paperwork processing.
Take Presbyterian Manors of Mid-America (PMMA), for instance.
The healthcare organization was accustomed to new employee onboarding taking hours. After all, new hires had to fill in 30–40 forms. To PMMA, this wasn’t a workflow bottleneck — it was an inevitably slow part of the process.
However, by implementing frevvo forms, now new hires at PMMA only have to fill out their information once and all the forms auto-populate. This has saved hours of data entry and significantly sped up onboarding.
Unfortunately, there’s no easy way to identify chronic bottlenecks. You’ll simply need to assess each stage of your process, asking whether new solutions, like frevvo, can help cut out unnecessary actions.
Short term bottlenecks
A short term bottleneck is a little easier to notice as its effects jam up the production line like paper stuck in a printer.
These bottlenecks are unexpected and last-minute and usually arise due to poor planning or bad management.
A short term bottleneck is often due to manual processes going wrong, resulting in human error or delays.
While short term bottlenecks can be problematic when they occur, they’re only really an issue if there is no protocol to remedy the issue.
For example, say your company delivers frozen foods and your refrigerated truck breaks down. This will cause a minor delay if you can send out a new refrigerated truck and transfer the goods across.
But, if you don’t have a spare truck, you’ll have a huge problem of wasted defrosted food and angry customers missing their orders.
While you won’t need a magnifying glass to spot short-term blockages when they occur, you’ll need a strong risk management plan to identify where a potential bottleneck might occur before they happen.
Infrastructure bottlenecks
Infrastructure bottlenecks are blockages in the basic physical and organizational structures and facilities of your company. These hold-ups can prevent certain operations from occurring.
Typical examples of infrastructure bottlenecks include:
- Inadequate storage facilities
- Vehicle shortage
- A lack of appropriate software
Regulatory bottlenecks
Regulatory bottlenecks occur when the regulations and policies that move processes along are incomplete, ineffective, or inappropriate.
Common regulatory bottlenecks include:
- Regulations not made at all
- Decisions not made on time
- Outdated policies that are irrelevant to new practices
- A lack of protocols for unexpected changes
Operational bottlenecks
Operational bottlenecks relate to blockages that occur within specific tasks during the process. These are usually temporary and are either capacity-related or efficiency-related.
Capacity-related bottlenecks occur when tools, resources, or staff are unavailable.
Efficiency-related bottlenecks occur when tools, staff, machines, technology, etc don’t work well enough or fast enough.
3. Analyze your process
Once you know how your processes work and what bottlenecks look like, you need to analyze your processes to make sure you’re managing bottlenecks that cause inefficiencies. Here’s how.
Look for common symptoms
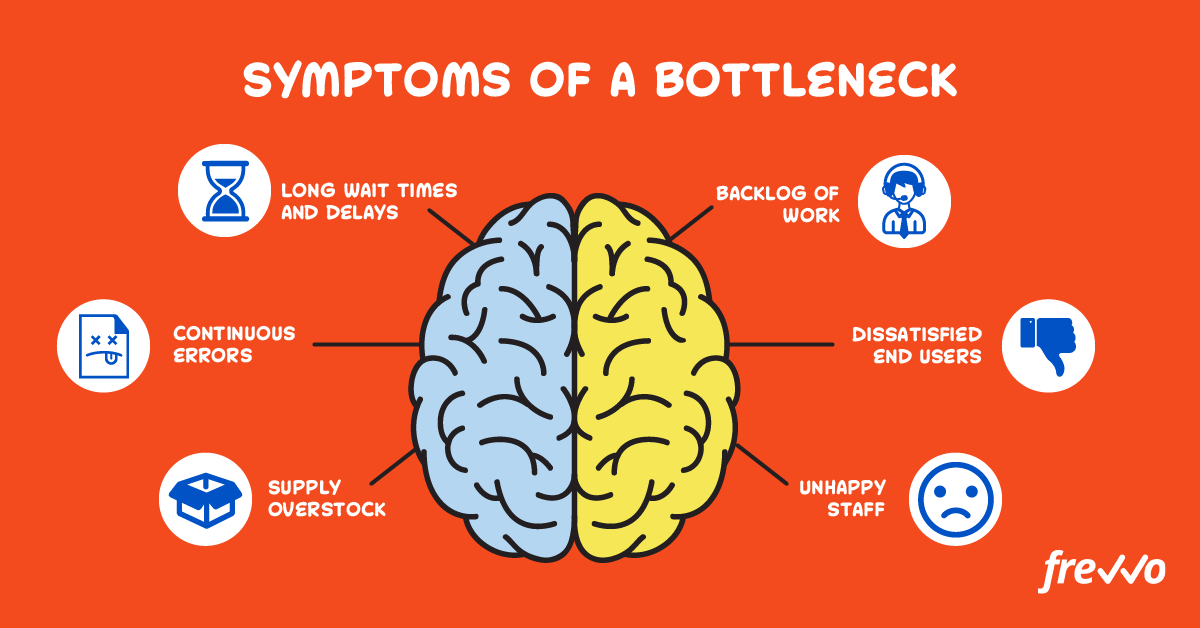
Here are some of the most typical negative effects from blockages in your processes.
Long wait times and delays
If your customers are queuing up, your inbox is backing up, or your paperwork is piling up, there’s delays caused by a bottleneck.
Take Central Wyoming College (CWC), for example.
Their purchase order (PO) process required approvers to manually approve all POs, meaning that staff had to spend hours waiting for approvals or chasing approvers. This meant long delays in purchasing much-needed supplies.
The remedy? frevvo forms enable CWC to automatically route POs to approvers so they can digitally sign all approvals. Automatic notifications now mean that approvers always sign approvals on time and staff don’t have to wait for supplies.
Continuous errors
Some actions, such as manual data entry, may bottleneck operation processes due to their propensity for error. Constant errors prevent processes from moving along until these mistakes are remedied.
This is what Aero Communications found.
When using manual paper forms for everyday processes, the technology firm experienced constant data entry errors and duplicate data. Lots of corrections meant extra time and costs.
By using frevvo forms, the technology firm was able to integrate its SQL database and automatically populate forms. Not only does this save time, it reduces errors and subsequent remedial work.
Backlog of work
When a process or production bottleneck occurs in your system, you’ll find that work starts to back up like a clogged drain.
Take a look at Medi USA.
The manual credit card application process was so slow and cumbersome that applications were piling up faster than staff could process them.
The medical manufacturer solved the problem with frevvo. Using digital forms, they can now auto-validate credit information and import data directly to their system. Thanks to frevvo, staff and IT resources are no longer overloaded and credit applications aren’t piling up.
Dissatisfied customers/end-user
If you’re seeing customer complaints, bad reviews, and high customer churn, you’re probably experiencing an existing bottleneck higher up the chain.
Take Canadian university, La Cité.
The clunky manual student registration process meant that students had to queue for over 20 minutes to get registration forms checked.
The result of this? Fewer students signed up for courses.
By switching to frevvo’s mobile forms, the school made it easier for students to sign up, resulting in a 700% increase in applications.
Unhappy staff
Experiencing high staff turnover or an increase in team complaints? Look for a potential bottleneck.
Look at teachers in the UK, for example.
The shortage of teaching staff has meant an increased workload for teachers. This huge workload is now the number one reason teachers quit the profession.
To help prevent this turnover, schools need to address this capacity-related bottleneck by employing more teachers.
Identify opportunities for automation
Simply put, automation helps to alleviate bottlenecks.
Process automation software like frevvo can reduce manual processing. This removes errors, speeds up processing, and reduces labor costs.
Ask yourself which stages of your process can switch from manual to automatic processing? Look for physical paper trails, hand-written approvals, and manual data entry.
Speak to the operators
The people working the processes know the most about what works well and what’s clogging the system.
Ask your suppliers, staff, and customers to identify the stress points. Find out which phases are too slow, where protocols are missing, and which mistakes happen most often.
Look at your competition
Your competitors can often give you keen insights into how to overcome bottlenecks and prevent backlash from blockages.
For example, if your company is the only firm offering next-day delivery, yet you often fail on this service, ask yourself why your competitors don’t do the same.
Equally, if you’re constantly experiencing the same problem, ask how your competition solves this to keep their staff and customers happy.
Draw a Fishbone Diagram
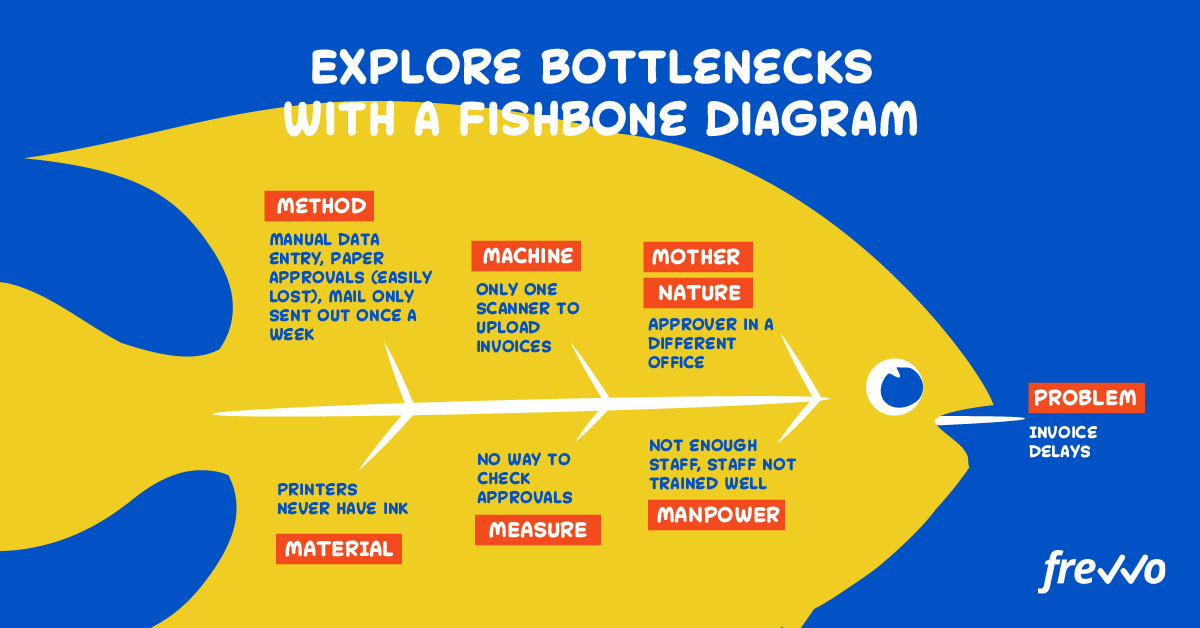
A fishbone diagram is a great visual tool for understanding which bottlenecks occur within different arms of the process.
The diagram invites you to explore blockages that occur at the point of:
- Machine – How does the technology, machinery, and tools work?
- Method – How is the process carried out?
- Manpower – Who’s involved in the process?
- Mother Nature – What is the environment like?
- Measurement – How is success measured?
- Materials – How and what resource is used?
Conclusion
Process improvement relies on you identifying the bottlenecks jamming up the system. By knowing how to identify bottlenecks, you can pinpoint the reasons for delays, extra costs, and dissatisfied stakeholders.
Remember, the symptoms of a process bottleneck may appear at different stages of a process if the root cause is having a knock-on effect. For truly effective bottleneck management, deep bottleneck analysis is vital.
Want an easy way to map your process analysis and iron out inefficiencies? Learn more about frevvo’s workflow analysis software.

